AI Week in Review 23.06.03
NVidia's Avatar Cloud Engine, Let's Verify Step by Step, and Voyager does Minecraft
Top AI Tools
Lexica.art is a website for generating, sharing, and viewing images created by AI image generation tools.
AI Tech and Product Releases
NVidia stole the new product release spotlight this week with some cool NVidia product announcements at Computex. Lots of hardware announcements for powering AI, including:
Nvidia’s GeForce RTX 4060 Ti GPU for gamers is now in full production
Full-volume production of GPU server HGX H100
Nvidia’s GH200 Grace Hopper is now in full production
NVidia also revealed Avatar Cloud Engine for conversational AI & NLP with video game characters. AI Breakfast on Twitter shared a demo of an AI-based Avatar, where the dialog is AI-generated.
NVIDIA’s new AI model “Neuralangelo” reconstructs 3D scenes from 2D videos. This is an incredible capability, and the demo of it is impressive:
Not a new release, but this OpenAI roadmap according to Sam Altman offers insight into what OpenAI is working on right now and planning to release soon. A key challenge is OpenAI is a victim of their own success. They are “extremely GPU-limited” and this is preventing them from rolling out some features like longer context windows and multi-modality. What to expect out of OpenAI in 2023:
Reduce cost of GPT-4. Make GPT-4 faster and cheaper.
Longer context windows, up to 1 million tokens.
Fine-tuning API - allowing custom fine-tuning up to GPT-4.
Stateful API - remembering the conversation history in the context.
Multi-modality may finally come to GPT-4 users in 2024, after more GPUs come online.
AI Research News
In a new paper Let’s Verify Step by Step, OpenAI researchers significantly improved the mathematical reasoning capabilities in GPT-4 by using process supervision, which gives feedback into a reward model on whether each intermediate reasoning step is valid or not.
The method showed great improvement over outcome-supervised reward models, which score whether a final answer is correct or not. The paper stated, “Our process-supervised model solves 78% of problems from a representative subset of the MATH test set.” This is a huge leap from prior SOTA scores of 50% on reasoning capabilities.
Since mathematical reasoning has been a big challenge for LLMs, this could yield huge improvements in how GPT-4 performs in science, math, and related difficult and challenging domains. It also could help with alignment to have reward models on the inner workings of each step as opposed to a full and final outcome. Sam Altman says it is a “positive sign for alignment.”
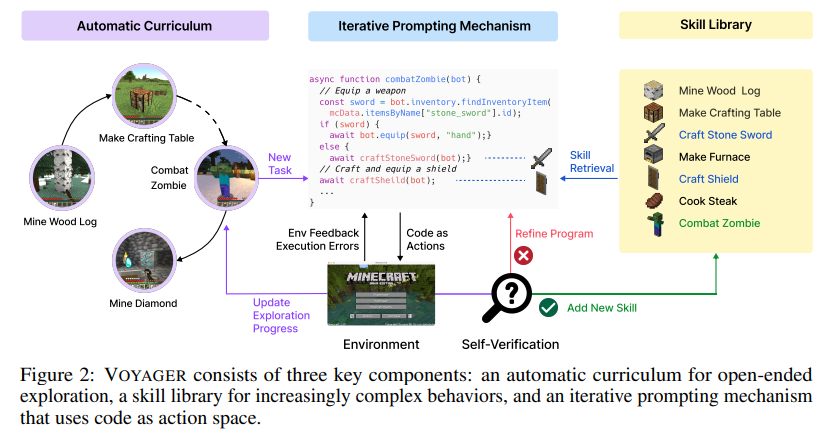
NVidia researchers present Voyager, An Open-Ended Embodied Agent with Large Language Models. Voyager is a learning agent that operates in Minecraft, which has proven to be a good substrate for developing virtual agents. It consists of three key components, shown below from the paper.
AI Business News
The uncomfortable truth of Microsoft’s Build Conference points out how much OpenAI and chatGPT has driven the product announcements at Microsoft Build. They are business co-dependents. All the major product announcements were around chatGPT, BingChat, or the various “co-pilot” features that rest on using OpenAI’s GPT-4.
On the one hand, this shows how much ChatGPT and OpenAI have become vital to Microsoft’s AI strategy. On the other, it fortifies some of the criticism against OpenAI about transforming from an open research lab to a closed for-profit subsidiary of Microsoft.
HP CEO says AI will significantly change the PC. "What we are working on is to build AI capabilities into the PC. So consumers or professionals will be able to run AI applications at the edge and will not have to run them on the cloud." - HP CEO Lores on quarterly earnings call.
AI contributed to nearly 4,000 job losses last month, according to a report from an outplacement firm that looked at jobs lost in layoffs. AI was responsible for 3,900, or roughly 5%, of the 80,000 jobs lost to layoffs in May.
Amr Awadallah shares his Waymo self-driving robotaxi ride in Twitter video clips:
AI Opinions and Articles
Bills regulating AI are bubbling up in Congress, as Rep Torres introduces bill requiring disclosure of AI content. Torres says of his bill: “The simplest place to start is disclosure. All generative AI—whether the content it generates is text or images, video or audio—should be required to disclose itself as AI.”
Military tech experts raise concerns about AI weaponization. Imagine if a military research project created a GPT-4 based AI agent network with the goal of “global security” and called it “Skynet”. I’m sure nothing will go wrong.
“Whether we’re talking about the Chinese building it, or us building it, or Iran building it … once it’s built, you can’t keep it secret. That’s just not going to happen. That’s not the way science works.” - retired Air Force Maj. Gen. William Enyart
A Look Back …
Erik Larsen on how AI changed around 2000 to adopt big-data machine learning AI:
Erik Larson: Basically starting around the year 2000, AI went from the old way of doing things to a kind of data-driven way. Basically we’re dealing now with what I call Big Data AI, which is basically “AI works the best when you have massive data sets.”
In the old way of doing AI, we would write rules … a deductive approach … It’s a way of specifying premises and then reaching a conclusion. Those inferences are rule-based because you actually write or specify the knowledge and then you reach the conclusion that way.
But the web had taken off a few years earlier. I mean I think the first commercial company was on the web in 1994. But the traffic really started to accelerate in terms of the growth of pages on the World Wide Web in 1995 to 2000. So all of a sudden there was all this data.
… We ended up with what we used to call empirical techniques or learning techniques with 10x, 100x, 1,000x, 1,000,000x the amount of data — and all of a sudden they were doing things that they wouldn’t do before. So there was a period where the AI community kind of slowly, and then really all at once, dropped the rule-based approaches and adopted the empirical methods or the machine learning approaches. So the strength is that you can do a lot with data. The weakness is that you need a lot of data to do anything basically, right?