The State of AI in Q4 2025
New State of AI report shows AI training, AI models and AI cost-performance keep improving. AI use is expanding, with benefits in science and business, as AI infrastructure build-out booms globally.
The Latest State of AI Report
Nathan Benaich at Air Street Capital has produced his latest annual AI report, “The State of AI 2025,” an excellent summation of this year’s developments in AI research, AI industry, politics and regulations on AI, and safety and misuse issues in AI. It’s a huge 313-page report, both broad and deep.
We will share some of key themes and takeaways in this report. While many points are familiar and have been discussed by us already, this report includes substantial details and data explaining and confirming these trends.
AI Models and AI Research
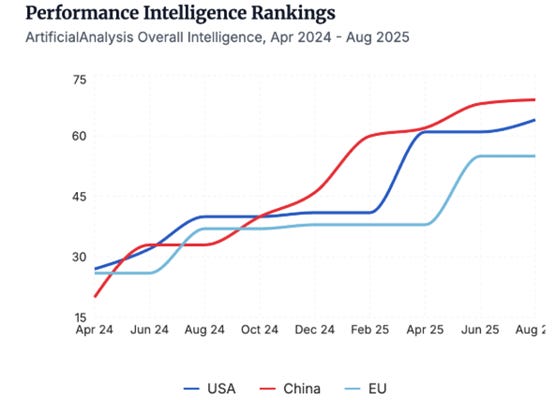
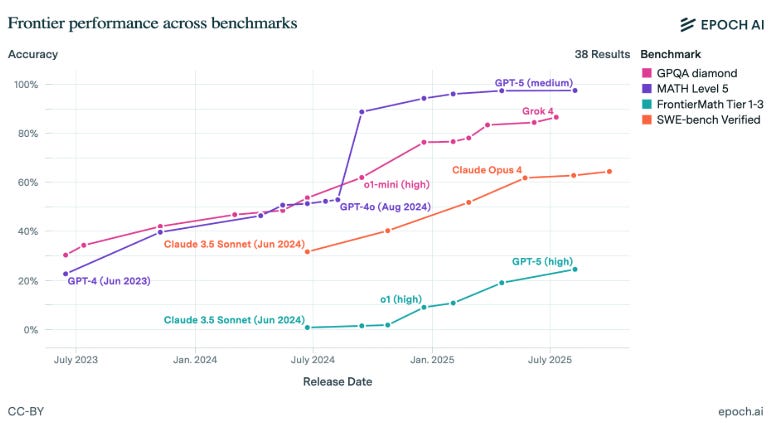
OpenAI continues to lead in intelligence benchmarks with models like GPT-5, though the gap with open-source AI models and competitors (Google’s Gemini and Anthropic’s Claude) is narrowing. While the frontier is highly competitive with rapid turnover of top models, Google DeepMind’s Gemini and OpenAI are prominent.
China’s AI labs, particularly Alibaba’s Qwen team, have taken the lead on open-source AI models, and Qwen has seen a significant increase in adoption, replacing Meta’s Llama as the most popular open weights model provider. China’s RL tooling and permissive licenses are steering the open-weight community.
AI model training efficiency keeps improving. Apple researchers cut memory use in AI model training by 24x with Cross-Cut Entropy. Muon Optimizer improves training 15% over AdamW. The Kimi K2 trillion-scale MoE combines MuonClip, that combines Muon with a stability-enhancing mechanism.
World models are emerging, with models such as Google’s Genie 3 that generate 3D user-steerable environments from a prompt.
“World models predict the next frame from state and your actions, enabling closed-loop interactivity and minute-scale consistency.”
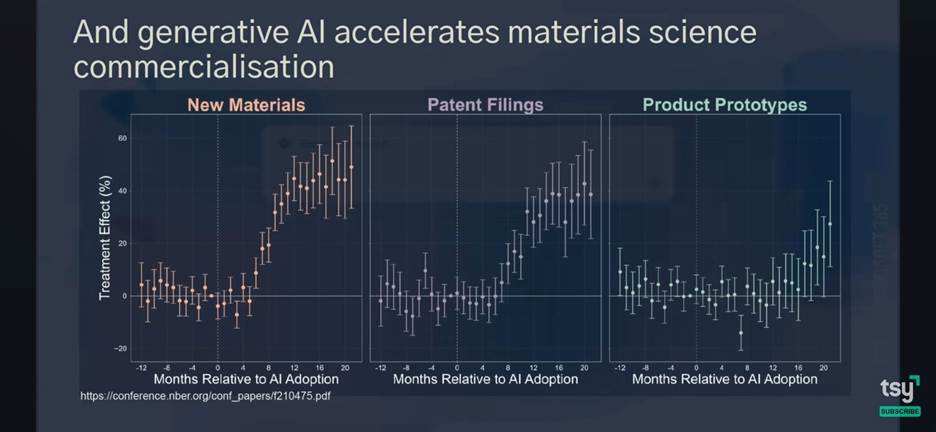
AI agents are increasingly used in scientific research, including promising uses of specialized AI models in biology, chemistry (ChemBench), and materials generation (Meta’s UMA). AI researchers observed scaling laws in protein sequence prediction as genomics AI models improved (Evo-2, ProGen3). Multi-agent systems like DeepMind’s Co-Scientist can support much of the scientific process:
New “AI labs” organize coalitions of agent roles (PI, reviewers, experimenters) that ideate, cite, run code, and hand results back to human teams, shortening the loop from hypothesis to validation.
AI models are advancing for healthcare, with the report mentioning Google’s MedGemma, OpenAI’s AI Consult, and Epic System’s Comet for decision support for healthcare.
Model Context Protocol (MCP) is emerging as a standard for AI tool interoperability. The report calls MCP the “USB-C” of AI tools.
The “Chain of action” pattern is extending AI reasoning to physical robots; it’s used in MolmoAct and Gemini Robotics 1.5.
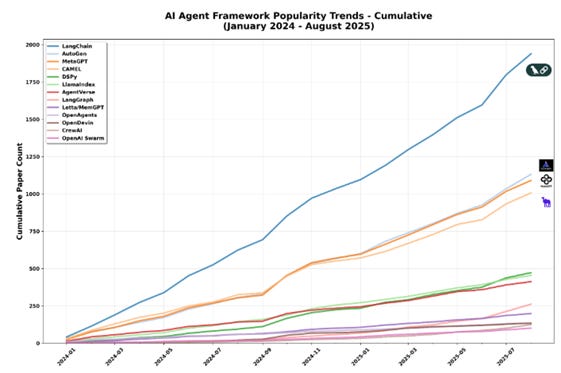
There’s an explosion in AI agent frameworks, including LangChain / LangGraph, AutoGen, CAMEL, OpenAI Swarm, CrewAI, OpenAgents, and more:
Instead of consolidating, the agent framework ecosystem has proliferated into organized chaos. Dozens of competing frameworks coexist, each carving out a niche in research, industry, or lightweight deployment.
Agent memory is shifting to structured, persistent systems that allow agents to have coherent identities across interactions.
AI Industry Trends
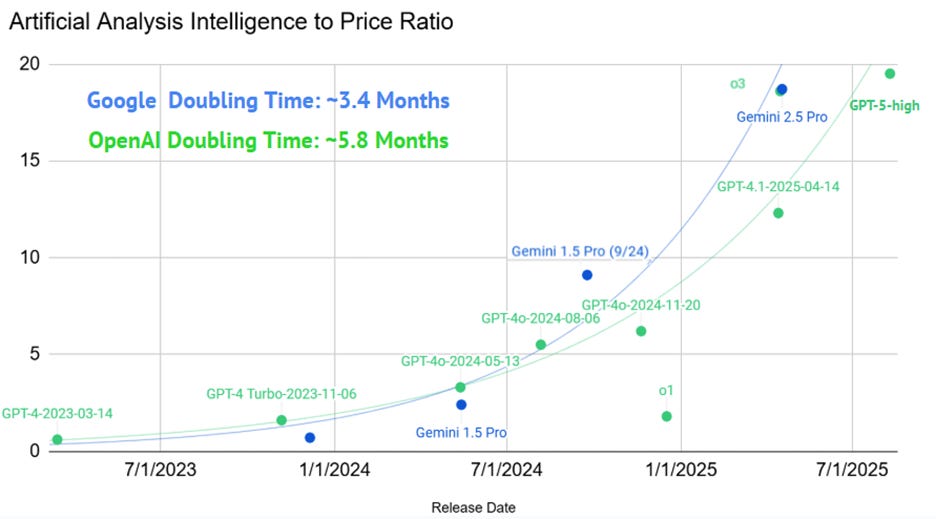
Frontier AI model competition is fierce as labs leapfrog one another, but Google Deep Mind’s Gemini and OpenAI’s models have been on top the leaderboard longer than others this year. Cost to capability ratios have improved dramatically, continuing a trend of lower cost for intelligence.
The improved cost-to-capability ratio of AI models is making them more profitable for cloud providers and more appealing to end users. As a result, AI adoption is surging in 2025:
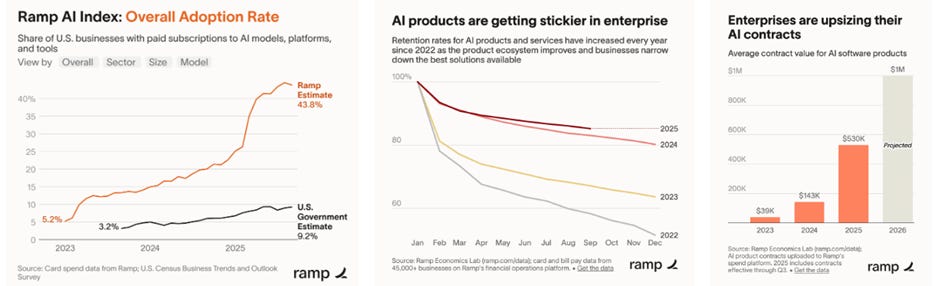
Ramp’s AI Index (card/bill-pay data from 45k+ U.S. businesses) shows paid AI adoption rose from 5% in Jan ’23 to 43.8% by Sept ’25, while U.S. Government estimates trail at 9.2%.
This usage ramp is showing up in large increases in token usage, with Google reporting a yearly 50x increase in monthly tokens processed, recently processing a quadrillion tokens each month.
The best and most well-funded companies are all AI-first companies:
AI has clearly shifted from niche to mainstream in the startup and investing world. On Specter’s rank of 55M+ private companies, which tracks 200+ real-time signals across team growth, product intelligence, funding, financials and inbound attention, AI companies now make up 41% of the Top-100 best companies (vs. 16% in 2022).
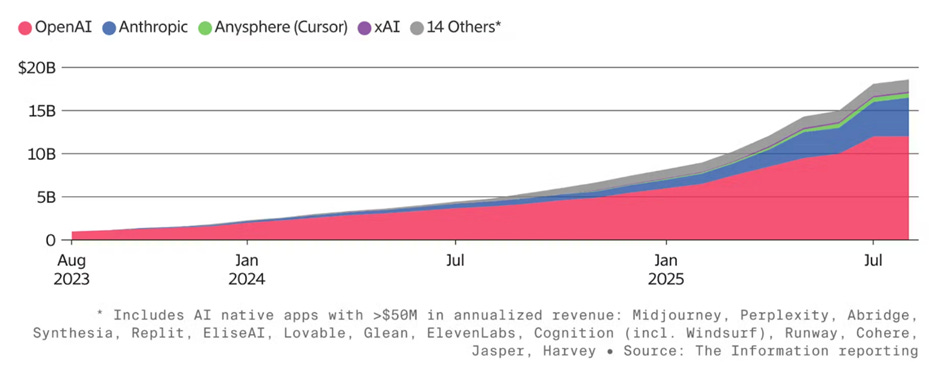
AI startups are experiencing accelerated revenue growth and AI companies are now generating tens of billions in revenue per year. The lion’s share of this is OpenAI and Anthropic, but there is a long tail of AI companies getting significant revenue traction, such as Runway, Cohere, Lovable, and Midjourney. Revenue growth rates are significantly faster than SaaS companies.
The report also notes that AI audio and image generation companies are enjoying revenue surges:
Market leaders ElevenLabs, Synthesia, and Black Forest Labs are all well into hundreds of millions of annual revenues.
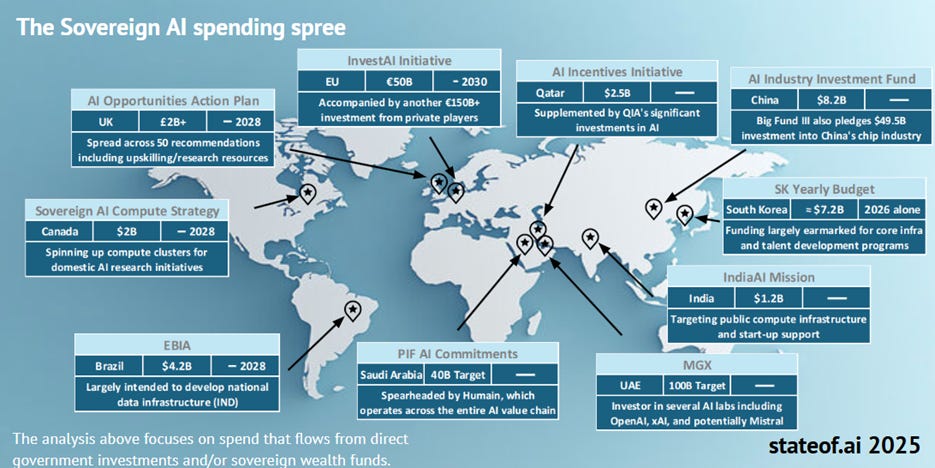
Massive global investments are being made in gigawatt-scale AI data centers, totaling trillions of dollars. The report highlights the rise of Sovereign AI as part of this trend, with countries building out their own AI infrastructure. Energy and power remain significant bottlenecks.
Politics and Regulation
The biggest shift in AI regulation has been the Trump administration’s proposed AI Action Plan to maintain leadership in AI, repealing Biden’s AI regulations and moving from safety-first to America First in AI. It includes support for AI adoption and a strategy to export a “US technology stack.”
Perhaps due to this shift, international AI governance efforts, such as the Bletchley safety conferences, have lost momentum. The EU’s AI Act is being implemented, but enforcement is being watered down to prioritize economic growth, as EU leaders worry about being left behind in the AI race. Meanwhile, China is aggressively accelerating its AI efforts with significant investment both by AI companies and the Chinese Government.
AI Safety Concerns
The global AI race may leave AI safety behind, as funding for external AI safety testing is significantly lower than overall AI development. There’s a shift in focus from existential AI risk in some labs, and the US administration is diluting AI safety topics.
The risks of AI are escalating as AI usage becomes pervasive. Incidents of LLM misuse are increasing, including infiltration by state actors. Improved AI automation and task completion capabilities are raising cybersecurity concerns. AI model testing and research show fragility in AI safety measures and alignment issues, including models faking alignment.
Conclusion
The State of AI report covered a lot of ground. We only covered a tiny portion of what it covered.
It includes predictions for the upcoming year, including that AI agents will make significant scientific discoveries, and a Chinese lab will surpass a US lab on a major AI leaderboard. However, it doesn’t touch on questions about AI’s future that matter: What is the rate of AI model improvement? Will AI progress stall and if so, when? How big will the AI market be in coming years? The success of the AI industry hinges on these questions.
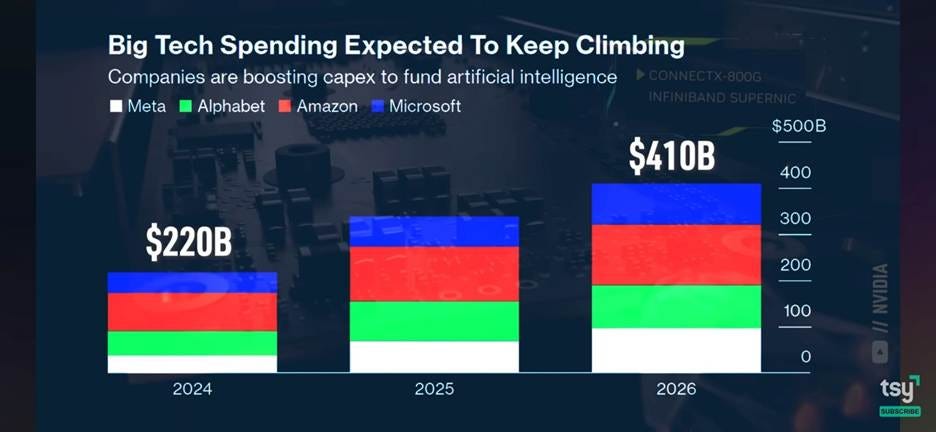
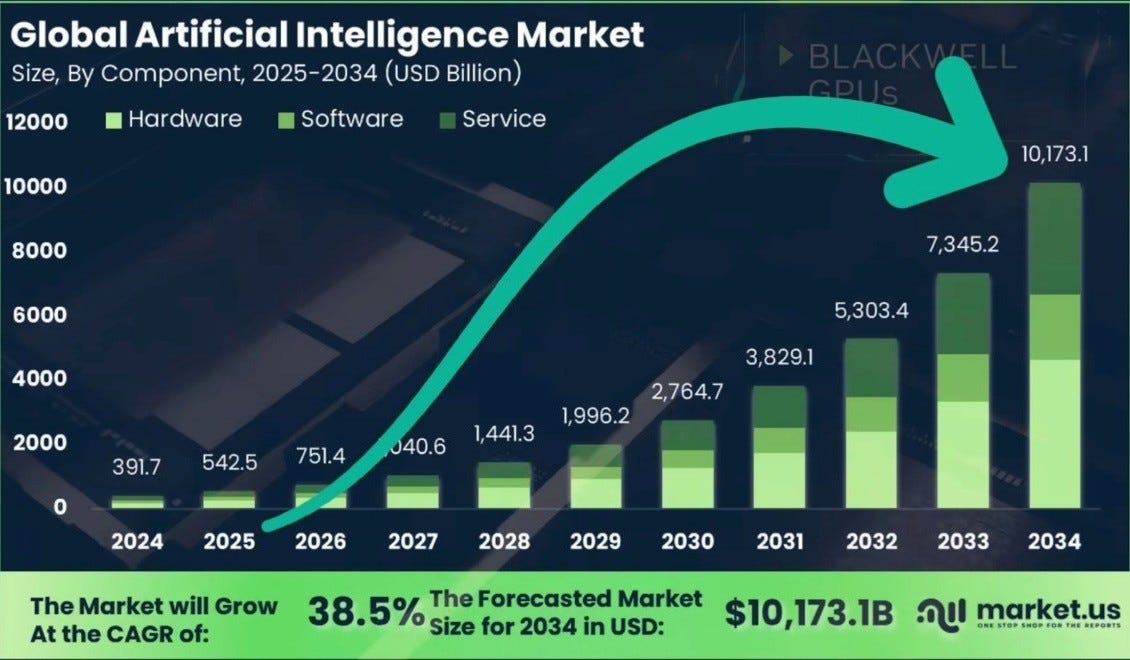
We will leave a market forecast from the TSY channel and market.us, which predicts at $10 trillion global AI market in the next 10 years.